Date Taken: Fall 2025
Status: Work in Progress
Reference: LSU Professor Dong Lao, ChatGPT
Linear algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with vectors, vector spaces, and linear transformations. It is fundamental to many areas of science and engineering, particularly in machine learning and artificial intelligence.
A vector is an ordered list of numbers that can represent a point in space or a direction. Vectors can be added together and multiplied by scalars (numbers) to create new vectors.
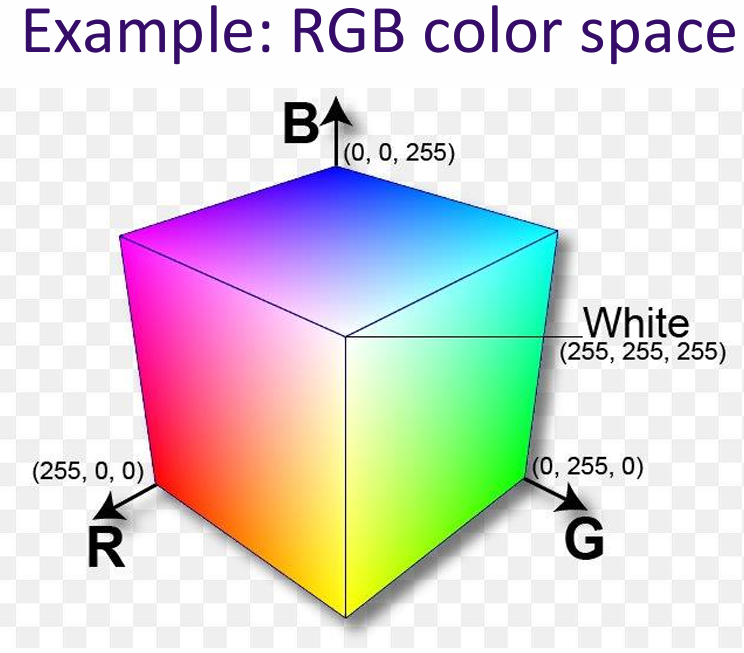
A group of real numbers, a coordinate in a high-dimensional space, a direction (displacement) in a high-dimensional space
Example: RGB color space

Why we care about vectors in AI? Vectors are essential in AI because they allow us to represent complex data in a structured way. For example, in image processing, an image can be represented as a vector of pixel values. This representation makes it easier to apply mathematical operations and algorithms to analyze and manipulate the data.
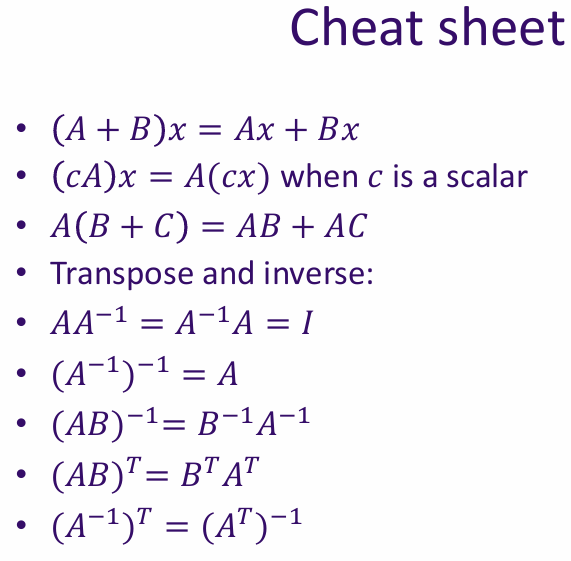
Associativity is a property of certain operations that allows us to group operands in different ways without changing the result. In the context of vectors, addition is associative:
(u + v) + w = u + (v + w)
Commutativity is a property of certain operations that allows us to change the order of operands without changing the result. In the context of vectors, addition is commutative:
u + v = v + u
Distributivity is a property that relates two operations, typically addition and multiplication. In the context of vectors, scalar multiplication is distributive over vector addition:
a(u + v) = au + av
In the context of vectors, scalar multiplication is distributive over field addition:
(a + b)v = av + bv for all a, b ∈ F and v ∈ V
The identity element is a special element in a vector space that, when combined with any vector, leaves the vector unchanged. In the context of vector addition, the identity element is the zero vector (0 ∈ V):
v + 0 = v for all v ∈ V
Scalar multiplication is compatible with field multiplication, meaning that multiplying a vector by a scalar and then by another scalar is the same as multiplying the scalars together first:
a(bv) = (ab)v for all a, b ∈ F and v ∈ V
The identity element of scalar multiplication is the number 1. When a vector is multiplied by 1, it remains unchanged:
1v = v for all v ∈ V, where 1 denotes the multiplicative identity in the field F.
The inner product (or dot product) is a way to measure the similarity between two vectors. It is calculated by multiplying corresponding elements of the vectors and summing the results.
Example: If u = [1, 2, 3] and v = [4, 5, 6], then the inner product u · v = 1*4 + 2*5 + 3*6 = 32.
Why we care about inner products in AI? Inner products are important in AI because they provide a way to measure similarity between data points. For example, in recommendation systems, the inner product can be used to determine how similar two users are based on their preferences.
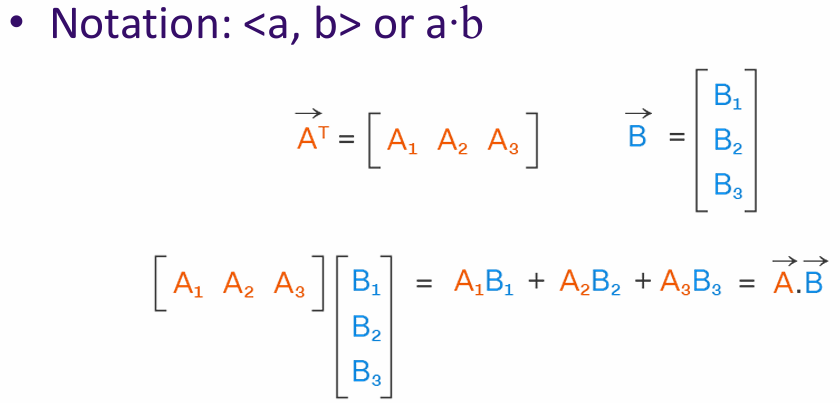
Cosine similarity is a measure of similarity between two non-zero vectors. It is defined as the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. When two vectors are orthogonal (orthogonal means perpendicular) to each other, a · b = 0
similarity(a,b) = \( \frac{a \cdot b}{|a| \, |b|} \)
Why we care about cosine similarity in AI? Cosine similarity is particularly useful in high-dimensional spaces, where it helps to identify similar items regardless of their magnitude. This is important in applications like document similarity, where the length of the documents may vary significantly.
The norm of a vector is a measure of its length or magnitude. Length of a vector: \[ \|x\|_2 = \sqrt{x_1^2 + x_2^2 + \cdots + x_n^2} = \left( \sum_{i=1}^{n} x_i^2 \right)^{1/2} \]
Lₚ norm: \[ \|x\|_p = \left( \sum_{i=1}^{n} |x_i|^p \right)^{1/p} \]
Unit ball: \[ \|x\|_p = \left( \sum_{i=1}^{n} |x_i|^p \right)^{1/p} \]
What is L₀ norm? An L₀ norm is a measure of the number of non-zero elements in a vector. It is not a true norm because it does not satisfy the properties of a norm, but it is often used in sparse representation and compressed sensing.
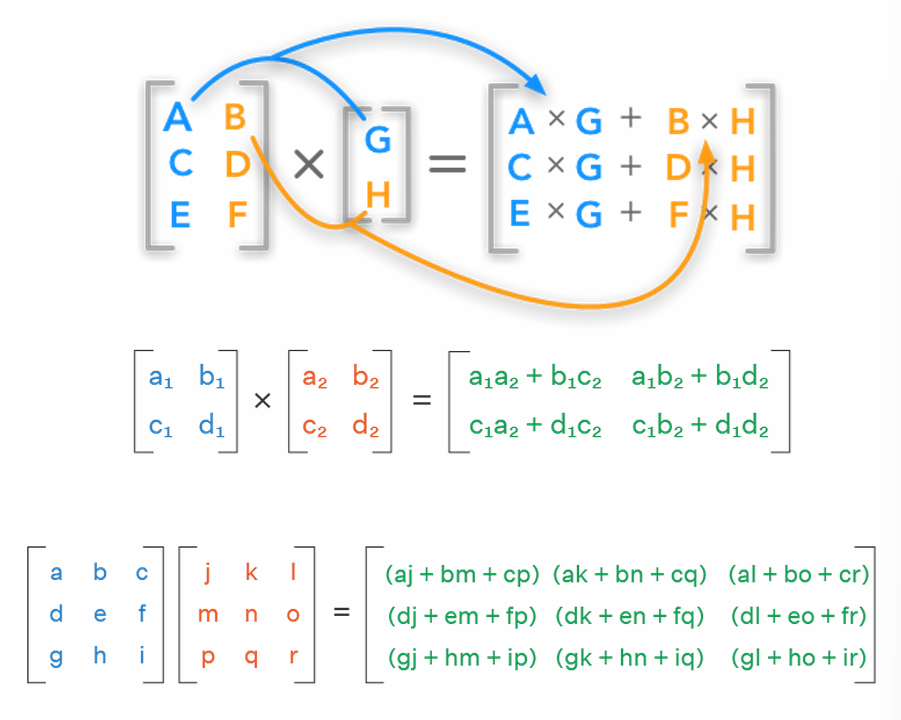
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. Matrices can be added together, multiplied by scalars, and multiplied by other matrices.
A matrix is a linear transformation that maps vectors from one vector space to another.
A linear transformation is a function between two vector spaces that preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. In other words, if T is a linear transformation, then for any vectors u and v, and any scalar a:
Linear transformations can be represented using matrices. If A is a matrix representing a linear transformation T, then for any vector v: \[ T(v) = Av \]
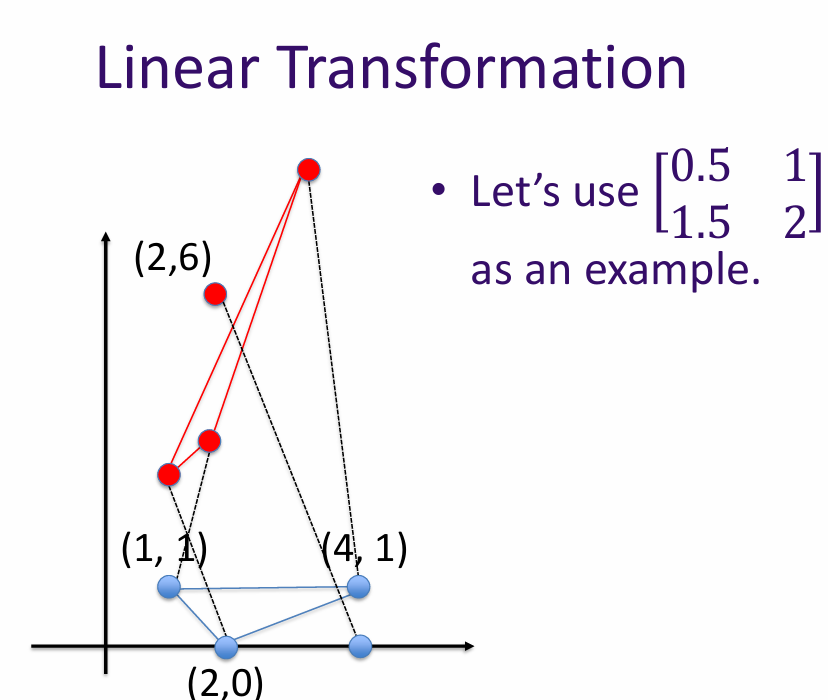
The rank of a matrix is the dimension of the vector space generated by its rows (or columns). In other words, it is the maximum number of linearly independent row (or column) vectors in the matrix.
Why do we care about rank in AI? The rank of a matrix can provide insights into the data it represents. For example, in dimensionality reduction techniques like PCA (Principal Component Analysis), the rank helps determine the number of principal components to retain.
\[ \text{rank} \begin{bmatrix} 0.5 & 1 \\ 1.5 & 2 \end{bmatrix} = 2 \quad \text{(It maps to a 2D space)} \] \[ \text{rank} \begin{bmatrix} 0.5 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} = 1 \quad \text{(It maps to a 1D space)} \]
An identity matrix is a square matrix with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere. \[ I = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \quad \text{(It always maps the vector to itself)} \]
Scaling by c: \[ cI = \begin{bmatrix} c & 0 \\ 0 & c \end{bmatrix} \]
It is denoted as Iₙ for an n x n identity matrix. The identity matrix has the property that when it is multiplied by another matrix, it leaves the other matrix unchanged: \[ I_n A = A I_n = A \]
Identity matrices are important in linear algebra and are used in various applications, including solving systems of linear equations and in the context of neural networks.
(x,y) = \( (r*\cos(\theta), r*\sin(\theta)) \)
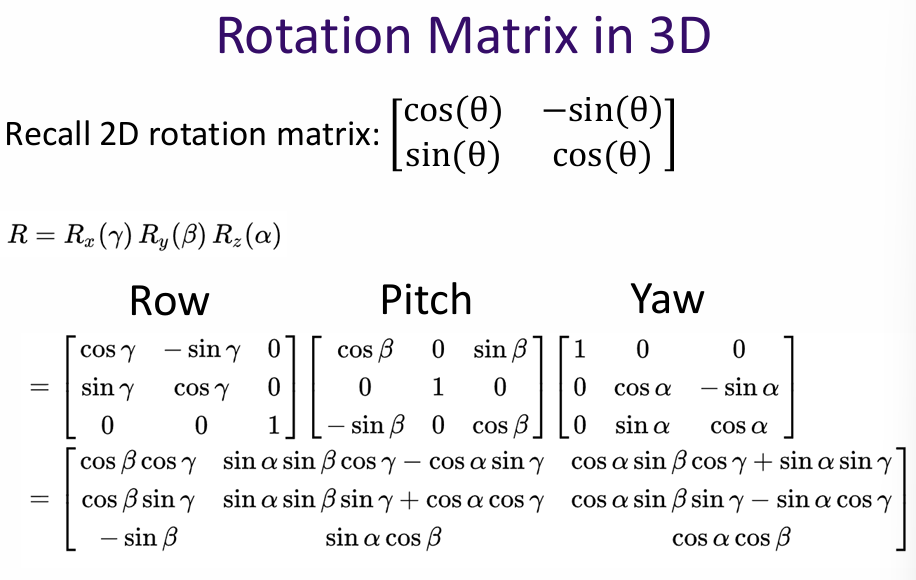
A rotation matrix is a matrix that is used to perform a rotation in Euclidean space. For example, in 2D space, a rotation matrix for an angle θ is given by: \[ R(\theta) = \begin{bmatrix} \cos(\theta) & -\sin(\theta) \\ \sin(\theta) & \cos(\theta) \end{bmatrix} \]
Rotating back by -θ would be done using the inverse rotation matrix:
\(
R(-\theta) =
\begin{bmatrix}
\cos(-\theta) & -\sin(-\theta) \\
\sin(-\theta) & \cos(-\theta)
\end{bmatrix}
\) = \(
\begin{bmatrix}
\cos(\theta) & \sin(\theta) \\
-\sin(\theta) & \cos(\theta)
\end{bmatrix}
\), BA = I, B = A⁻¹
A simple neural network consists of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Each layer is made up of neurons (or nodes) that process the input data and pass it on to the next layer.
The connections between the neurons are represented by weights, which are adjusted during the training process to minimize the error between the predicted output and the actual output.
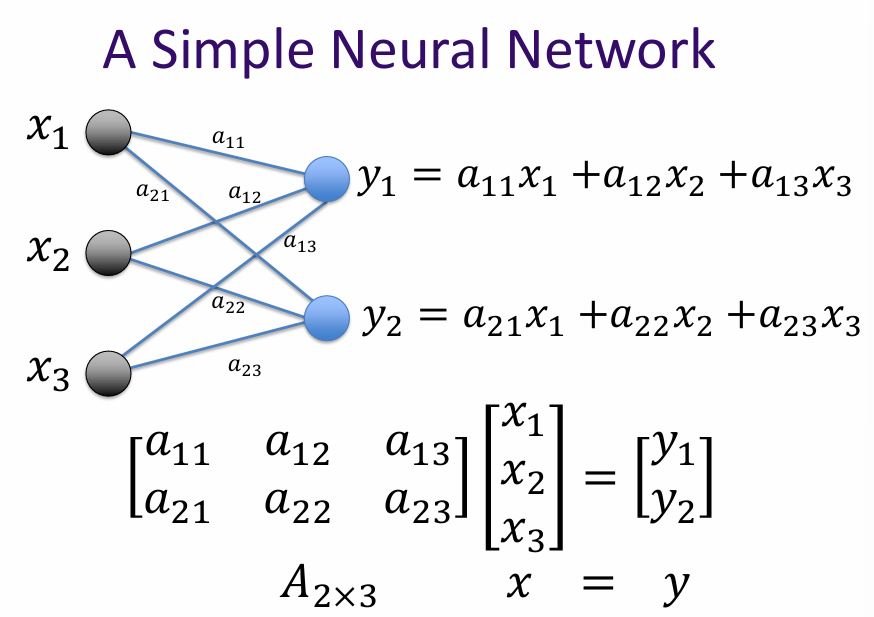
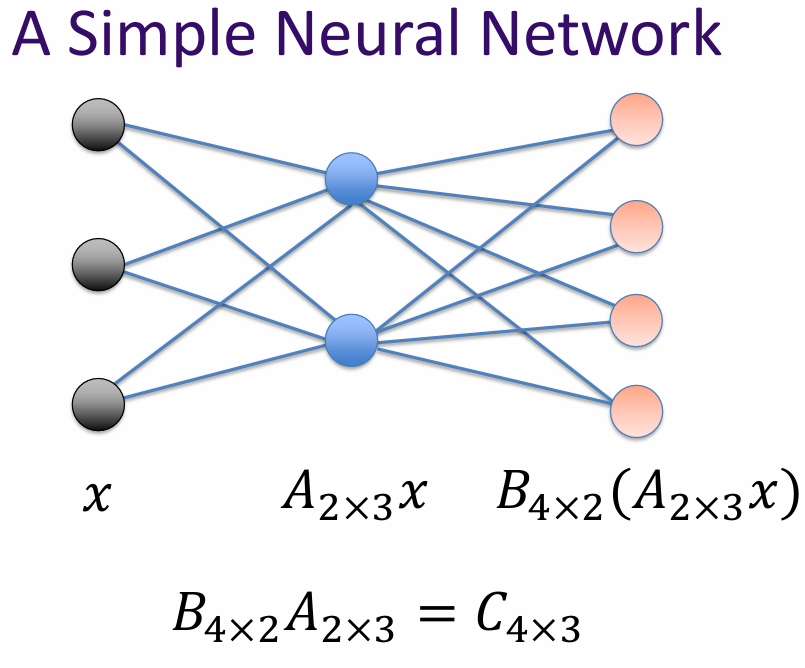
What is matrix? A matrix is a linear transformation represented in a structured format, typically as a rectangular array of numbers. In the context of AI and machine learning, matrices are used to represent and manipulate data, perform linear transformations, and facilitate various mathematical operations.