Intro To Cyber
Lecture 1 & 2
Date Taken: Fall 2025
Status: Completed
Reference: LSU Professor Joseph Khoury, ChatGPT
Summary
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computers, networks, and digital information from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage.
It involves preventing, detecting, and responding to threats like viruses, malware, phishing, ransomware, and hacking attempts.
The key concepts in cybersecurity are summarized by the CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, which provide a framework for designing and implementing security measures.
Confidentiality
Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized individuals or systems.
It prevents unauthorized disclosure of data, protecting privacy and proprietary information.
Integrity
Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and trustworthy.
Unauthorized modification or corruption of data is prevented, and users can rely on its authenticity.
Examples include: Hashing, Digital Signatures, Certificates, Non-repudiation.
- Hashing: A process that transforms input data into a fixed-size string of characters, which is typically a digest that is unique to the input data.
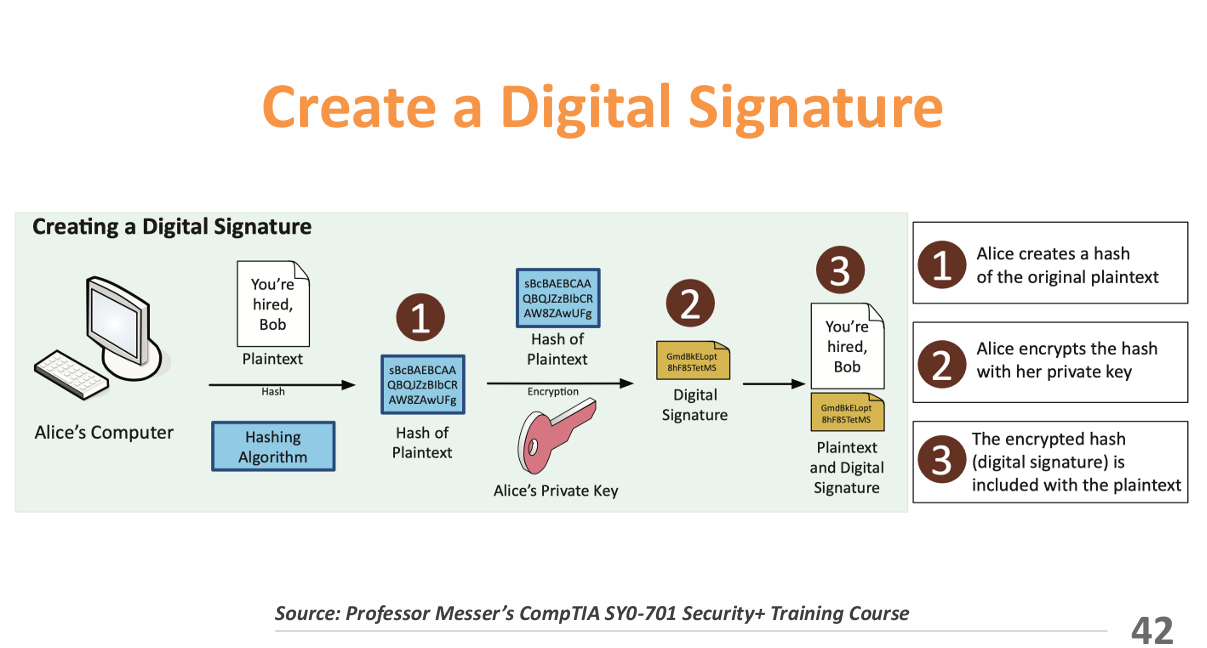
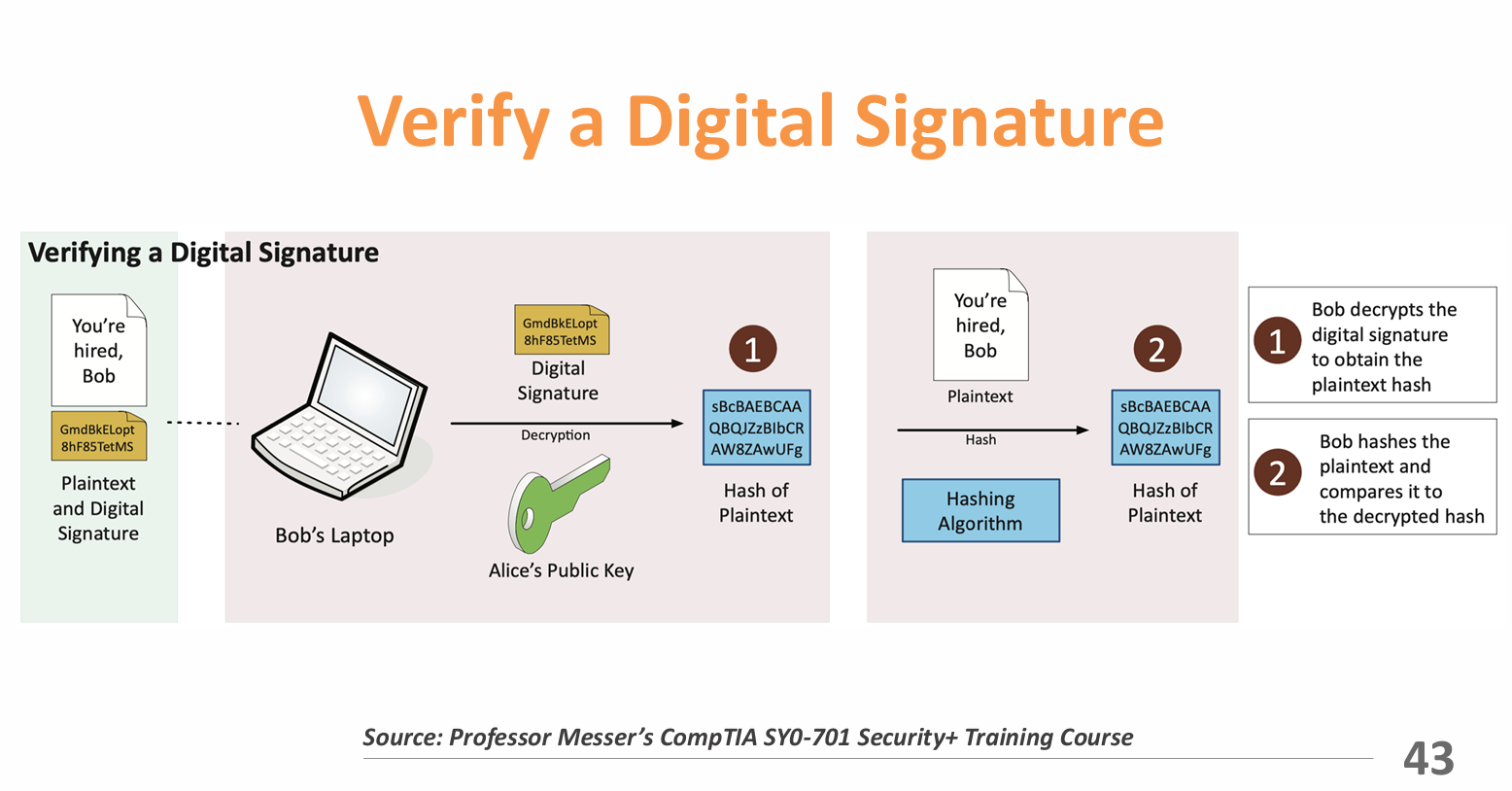
- Digital Signatures: A cryptographic technique that allows the sender of a message to sign it digitally, providing proof of authenticity and integrity.
- Certificates: Digital documents that bind a public key to an individual or organization, allowing for secure communication and authentication.
- Non-repudiation: A security principle that ensures a party cannot deny the authenticity of their signature on a document or a message.
Availability
Availability ensures that authorized users can access information and systems when needed.
Systems must remain operational, resilient, and recoverable from failures or attacks.
- Redundancy: Duplicate systems or components that ensure continued operation in case of hardware or software failures.
- Fault Tolerance: Systems designed to operate correctly even when one or more components fail.
- Patching: Regular updates to software and systems to fix security vulnerabilities and maintain stable operation.
General Security Concepts (Lecture 1 & 2)
Security Controls
Security controls are safeguards or countermeasures designed to protect information systems, networks, and assets.
They aim to reduce risks by preventing, detecting, or mitigating threats and vulnerabilities.
Controls are grouped into three main categories:
- Administrative Controls: Policies, procedures, and guidelines that define organizational security standards, such as employee training, access policies, and incident response plans.
- Technical Controls: Tools and technologies like firewalls, encryption, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems that enforce security at the hardware or software level.
- Physical Controls: Measures that protect physical assets, such as security guards, locks, badges, fences, surveillance cameras, and environmental protections (fire or flood systems).
Control Categories
Security controls are organized to provide comprehensive protection and include the following categories:
- Technical Category: Controls that use technology to reduce risks, such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
- Managerial Category: Controls that focus on management and governance, including risk assessments, security policies, and compliance management.
- Operational Category: Controls that implements by people instead of technology, such as security awareness training and incident response procedures.
- Physical Category: Controls that protect the physical environment, including locks, guard shacks, fences, and surveillance cameras.
Types of Security Controls
- Preventive: Measures designed to stop security incidents before they occur. Examples include firewalls, access restrictions, and employee security awareness programs. Administrative, technical, and physical measures to proactively stop attacks or unauthorized activity.
- Deterrent: Mechanisms that discourage malicious actions by making attacks costly or risky, e.g., warning banners, visible cameras, and legal notices. Controls that create psychological or visible obstacles to discourage malicious actions.
- Detective: Measures to identify and detect incidents as they happen, such as intrusion detection systems, audit logs, and surveillance cameras. Continuous monitoring and auditing to detect anomalies or breaches promptly.
- Corrective: Steps taken to correct or restore systems after an incident, like restoring backups, patching vulnerabilities, or reconfiguring affected systems. Actions and tools to recover systems and data after a security incident.
- Compensating: Alternative measures used when primary controls are unavailable or insufficient, like using multi-factor authentication when biometrics are unavailable. Alternative methods to maintain security when primary controls cannot be applied.
- Directive: Policies, guidelines, and signage that guide user behavior and ensure compliance with security practices.
Managing Security Controls
- Risk Assessment: Identify and evaluate threats and vulnerabilities to determine appropriate controls.
- Control Selection: Choose the most effective safeguards based on risk, regulatory requirements, and organizational objectives.
- Implementation: Properly deploy and configure security measures to integrate with the organization's environment.
- Monitoring: Continuously observe controls for effectiveness and detect potential issues through audits and real-time monitoring.
- Improvement: Update and enhance controls to address emerging threats and evolving risks.
Physical Security
Physical security protects buildings, facilities, equipment, and personnel from unauthorized access, theft, and environmental hazards.
It ensures the safety of assets and personnel, preventing damage or disruption to operations.
Key Components:
- Access Control: Locks, security personnel, keycards, and biometric systems to limit entry to authorized personnel.
- Surveillance: Cameras, motion sensors, and alarms to monitor activity and detect potential threats.
- Environmental Controls: Systems protecting against fire, floods, extreme temperatures, and other environmental risks.
- Security Policies: Procedures for visitor management, asset protection, and emergency response.
- Training and Awareness: Educating staff on physical security measures and their responsibilities in maintaining a safe environment.
Examples:
- Fences and Gates: Physical barriers to prevent unauthorized access to facilities.
- Security Guards: Personnel who monitor premises and respond to incidents.
- Surveillance Cameras: Monitor activity and provide evidence in case of breaches.
- Alarm Systems: Notify security teams immediately when unauthorized access is detected.