Intro To Cyber
Lecture 3
Date Taken: Fall 2025
Status: Completed
Reference: LSU Professor Joseph Khoury, ChatGPT
Access Control
Definitions
- NIST IR 7298: The process of granting or denying requests to obtain and use information and services based on access rules and authorization.
- RFC 4949: Regulates system resource usage according to a security policy, allowing access only to authorized users, processes, or devices.
AAA Framework
-
Authentication: Verifying identity using passwords, certificates, or tokens.
- Automated devices may authenticate using digital certificates for large-scale management.
- Certificates ensure secure access to services like VPNs and management software.
-
Authorization: Determining which resources an authenticated user or device can access.
- Role-based or attribute-based authorization simplifies access management in large environments.
-
Accounting (Auditing): Logging resource usage, such as login time, activity, and logout, for monitoring and compliance.
- Ensures that only authorized systems access sensitive information and tracks all activity for auditing purposes.
Access Control Policies
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): Access granted based on identity and rules defined by owners.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Access based on security labels compared to user clearances.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Permissions assigned according to organizational roles.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Access determined by user, resource, and environment attributes.
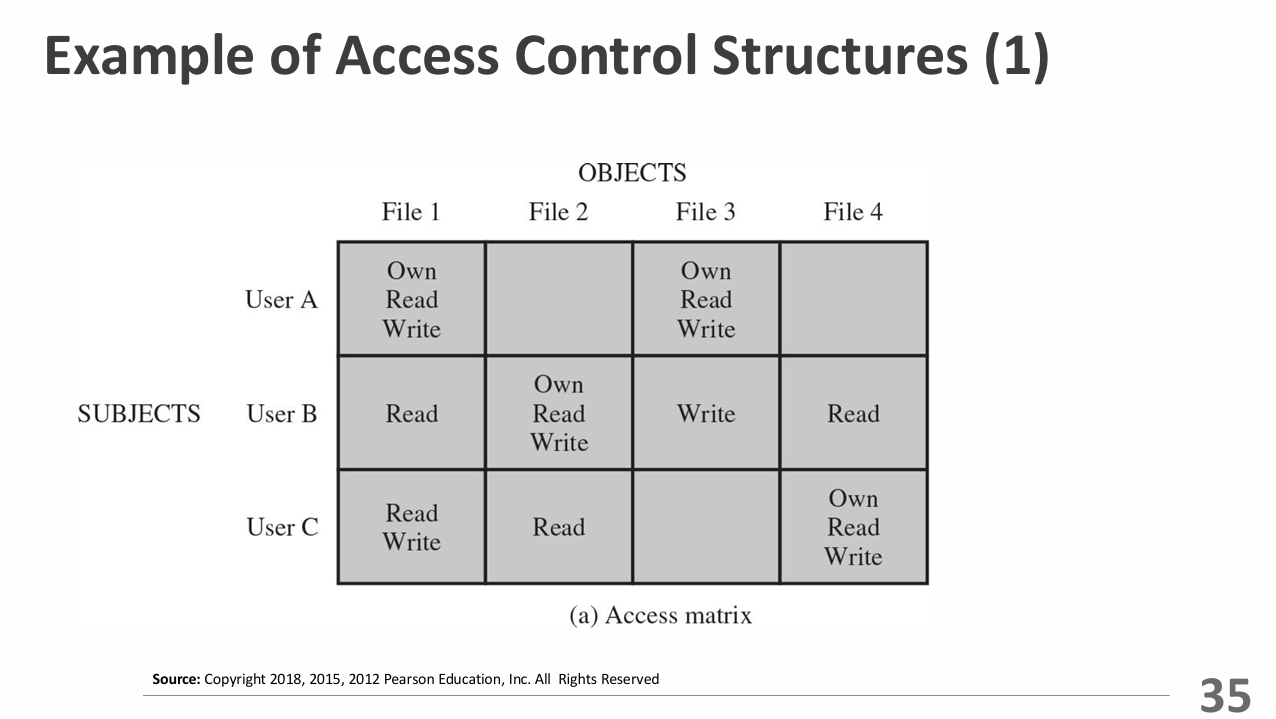
Subjects, Objects, and Access Rights
- Subject: Entity (user or device) capable of accessing objects. Three classes: Owner, Group, World.
- Object: A resource to which access is controlled. Entity used to contain and/or receive information.
- Access Rights: Permissions granted to subjects (Read, Write, Execute, Delete, Create, Search).
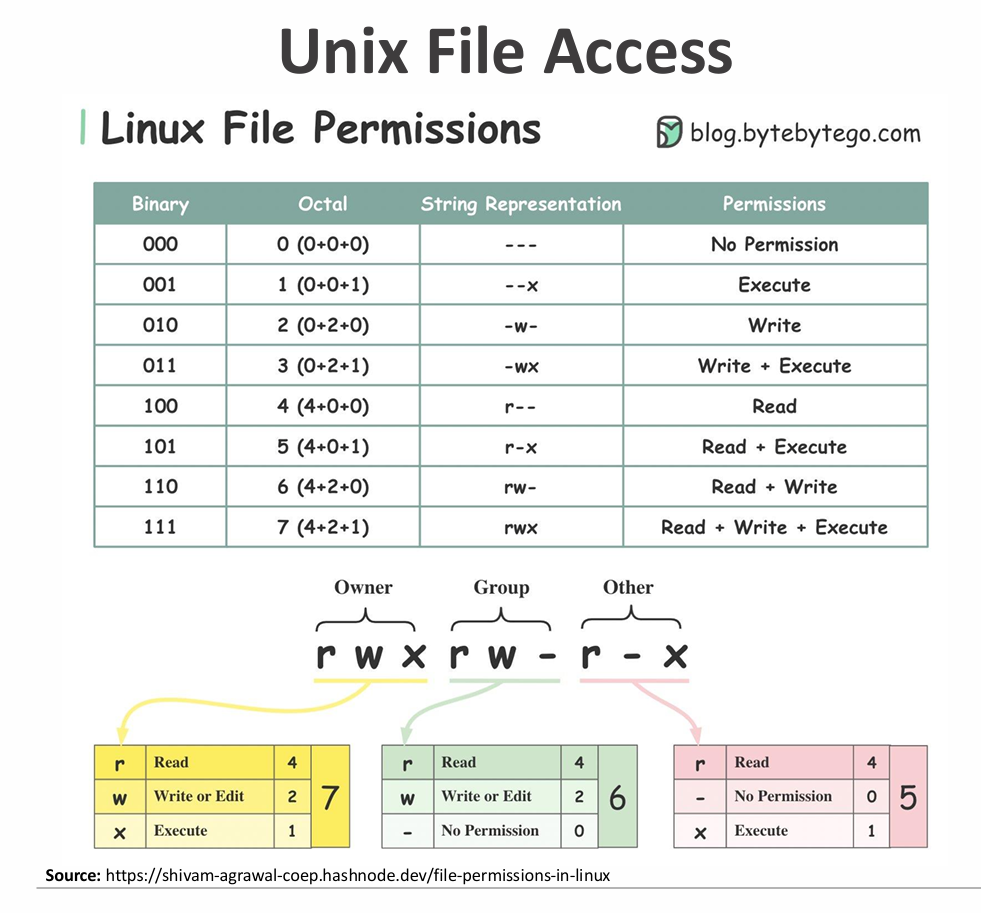
Unix File Access
UNIX files are managed using inodes (Index Nodes), which store metadata and control information for files.
- Inodes contain file attributes, permissions, and location information on disk.
- Multiple file names can link to the same inode, allowing shared access.
- Active inodes are loaded into memory for fast access by the operating system.
- The inode table on disk tracks all file inodes for the file system.
Zero Trust
Zero Trust means never automatically trust anything inside or outside your network.
Even if someone is already inside, they must prove who they are and have permission to access resources.
This approach checks every person, device, and process using things like multi-factor authentication, encryption, access controls, firewalls, and monitoring to keep the network secure.
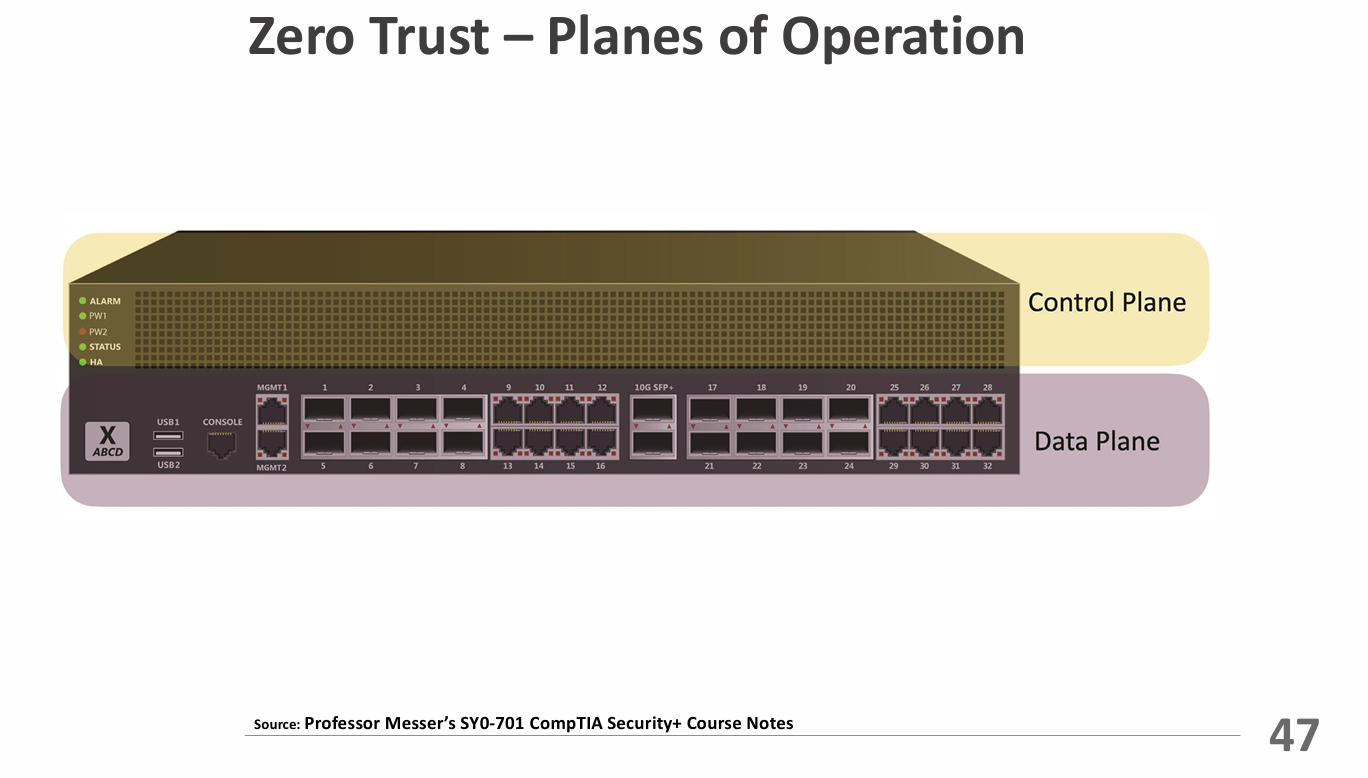
Planes of Operation
- Divide The Network Into Planes - Works for physical devices, virtual systems, and cloud setups.
- Example: Segmenting a corporate network into separate zones for finance, HR, and IT.
- Data Plane - Moves and handles the actual data—sends, encrypts, and routes packets.
- Example: A router forwarding data packets based on established rules (Control Plane).
- Control Plane - Tells the data plane what to do—sets rules, policies, and routing decisions.
- Example: A network administrator configuring routing protocols and access control lists (ACLs).
Security Zones
- Security isn't just one-to-one - Grouping systems into zones helps manage security better.
- Zones Show Trust Levels - hink about where traffic is coming from and going to—trusted vs. untrusted, internal vs. external networks, or different departments like Marketing, IT, Accounting, HR.
- Zones Control Access - Sometimes just being in the wrong zone is enough to block access. Some zones are automatically trusted.
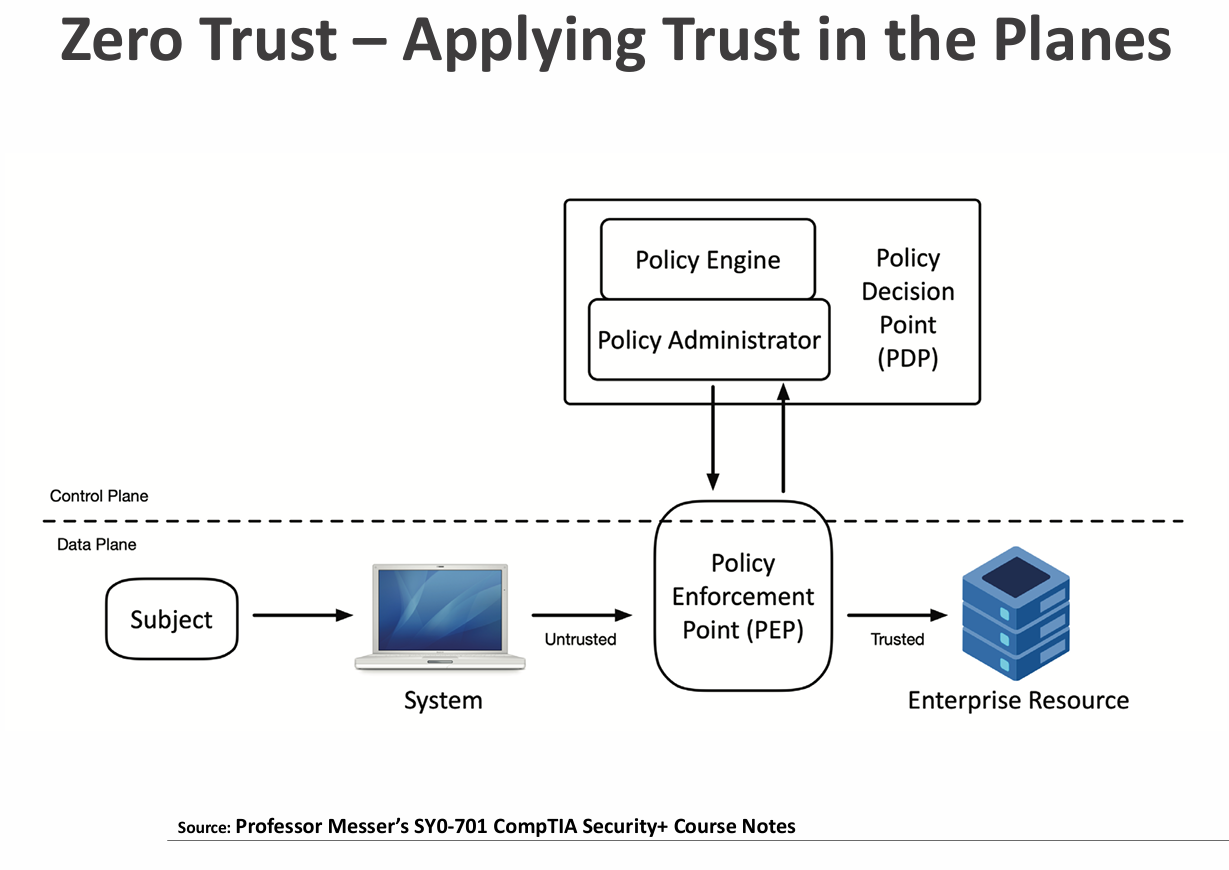
Policy Enforcement Point (PEP)
They acts like a gatekeeper for the network.
Decides what to do with connections: allows them, monitors them, or blocks them.
Can be made of serval parts working together.
Applying Trust In The Planes
- Policy Decision Point (PDP) - Decides whether someone or something should be allowed access.
- Policy Engine - Checks the rules and other information, then decides to allow, deny, or revoke access.
- Policy Administrator - Talks to the gatekeeper (PEP), gives access tokens or credentials, and tells the PEP whether to allow access. Can also make authentication stronger if needed.